

Whether to provide nucleus type labels, or binary nucleus labels. (mask and image) and return a dict with “image” and “mask” keys.
Transforms ( optional) – Data augmentation transforms to apply to images. Shuffle ( bool, optional) – Whether to shuffle images. If False, checks to make sure that data files exist in data_dir. If True, checks whether data files exist inĭata_dir and downloads them to data_dir if not.
Deepfocus io download#
For more information, see: Parametersĭata_dir ( str) – Path to directory where PanNuke data isĭownload ( bool, optional) – Whether to download the data. Contains 256px image patches from 19 tissue types with annotations for 5 PanNukeDataModule ( data_dir, download = False, shuffle = True, transforms = None, nucleus_type_labels = False, split = None, batch_size = 8, hovernet_preprocess = False ) ĭataModule for the PanNuke Dataset.
Deepfocus io how to#
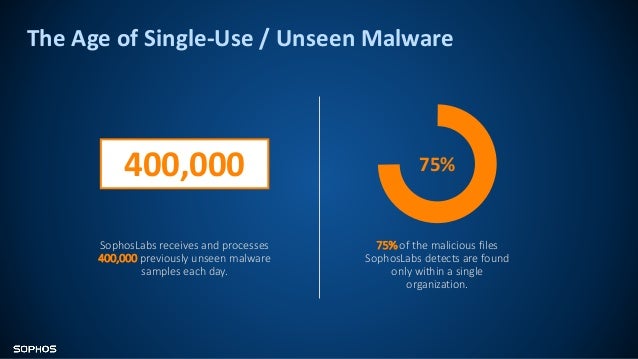
When trained and tested on two independent datasets, DeepFocus resulted in an average accuracy of 93.2% (± 9.6%), which is a 23.8% improvement over an existing method. DeepFocus was trained by using 16 different H&E and IHC-stained slides that were systematically scanned on nine different focal planes, generating 216,000 samples with varying amounts of blurriness. DeepFocus is built on TensorFlow, an open source library that exploits data flow graphs for efficient numerical computation.
Deepfocus io software#
The aim of this study is to develop a deep learning based software called, DeepFocus, which can automatically detect and segment blurry areas in digital whole slide images to address these problems. Moreover, this process is both tedious, and time-consuming. These areas are typically identified by visual inspection, which leads to a subjective evaluation causing high intra- and inter-observer variability. Moreover, these artifacts hamper the performance of computerized image analysis systems. Unfortunately, whole slide scanners often produce images with out-of-focus/blurry areas that limit the amount of tissue available for a pathologist to make accurate diagnosis/prognosis. The development of whole slide scanners has revolutionized the field of digital pathology.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
